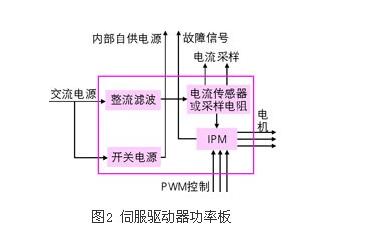
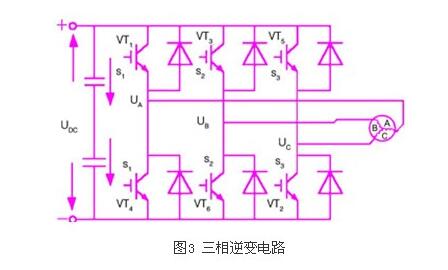
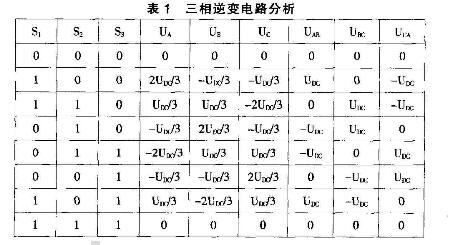
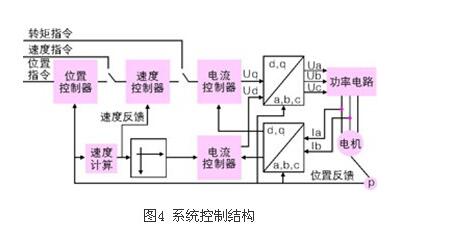
Modern AC servo systems have undergone a transition from analog to digital, digital control loops have become ubiquitous, such as commutation, current, speed and position control; using new power semiconductor devices, high-performance DSP plus FPGA, and servo-specific modules ( For example, the dedicated servo control engine launched by IR is not surprising. This paper mainly introduces the principle and control method of modern AC servo system. Let's take a look at it in detail. The AC permanent magnet synchronous servo driver mainly comprises a servo control unit, a power drive unit, a communication interface unit, a servo motor and a corresponding feedback detecting device, and its structural composition is shown in FIG. 1 . The servo control unit includes a position controller, a speed controller, a torque and current controller, and the like. Our AC permanent magnet synchronous drive integrates advanced control technology and control strategy, making it ideal for high-precision, high-performance servo drive applications. It also demonstrates powerful intelligence and flexibility for traditional drive systems. Unmatched. At present, the mainstream servo drives all adopt digital signal processor (DSP) as the control core, which has the advantages of implementing more complicated control algorithms, digitization, networking and intelligence. Power devices generally use a driver circuit designed with an intelligent power module (ipm) as the core. The driver circuit is integrated inside the ipm, and has fault detection and protection circuits such as overvoltage, overcurrent, overheat, undervoltage, etc., and soft is added in the main loop. Start the circuit to reduce the impact of the startup process on the drive. The servo drive can be roughly divided into two modules: the power board and the control board with relatively independent functions. The power board (drive board) shown in Figure 2 is a high-power part, which consists of two units. One is the power drive unit ipm for the motor drive, and the other is the switch power supply unit to provide digital and analog power for the entire system. The control board is the weak current part, which is the control core of the motor and the running carrier of the core control algorithm of the servo drive technology. The control board outputs the pwm signal through the corresponding algorithm as the driving signal of the driving circuit to change the output power of the inverter to achieve the purpose of controlling the three-phase permanent magnet synchronous AC servo motor. Power drive unit The power driving unit first rectifies the input three-phase electric power or the commercial power through a three-phase full-bridge rectifying circuit to obtain a corresponding direct current power. After rectification of three-phase electricity or mains, the three-phase permanent-magnet synchronous AC servo motor is driven by a three-phase sinusoidal pwm voltage type inverter. The entire process of the power drive unit can be simply the process of ac-dc-ac. The main topology circuit of the rectifier unit (ac-dc) is a three-phase full-bridge uncontrolled rectifier circuit. The inverter part (dc-ac) adopts the power device set drive circuit, the protection circuit and the power switch integrated intelligent power module (ipm). The main topology is a three-phase inverter circuit schematic diagram shown in Figure 3. Pwm (pulse width modulaTIon) changes the frequency of the inverter output waveform by changing the time during which the power transistors are alternately turned on, changing the on-off time ratio of the transistors in each half cycle, that is, by changing the pulse width. To change the size of the inverter output voltage value to achieve the purpose of regulating power. In Fig. 3, vt1 to vt6 are six power switch tubes, and s1, s2, and s3 respectively represent three bridge arms. The following is stipulated for the switching state of each bridge arm: when the upper arm switch tube is "on" (when the lower arm switch tube is necessarily "off" state), the switch state is 1; when the lower arm switch tube is "on" In the state (the lower arm switch tube must be in the "off" state at this time), the switch state is 0. The three bridge arms have only two states of "0" and "1", so s1, s2, and s3 form eight switch modes of 000, 001, 010, 011, 100, 101, and 111, of which the 000 and 111 switch modes make The inverter output voltage is zero, so this switch mode is called zero state. The output line voltage is uab, ubc, uca, and the phase voltage is ua, ub, uc, where udc is the DC power supply voltage, and the attached table analysis can be obtained according to the above. control unit The control unit is the core of the entire AC servo system, enabling system position control, speed control, torque and current controllers. In addition to its fast data processing capability, the digital signal processor (DSP) integrates a wealth of ASICs for motor control, such as a/d converters, pwm generators, timer counter circuits, and asynchronous communication. Circuits, CAN bus transceivers, and high-speed programmable static rams and large-capacity program memories. The servo drive implements vector control (vc) by using the field-oriented control principle (foc) and coordinate transformation, and controls the motor in combination with the sine wave pulse width modulation (spwm) control mode. The vector control of permanent magnet synchronous motor generally controls the stator current or voltage by detecting or estimating the position and amplitude of the rotor flux of the motor. Thus, the torque of the motor is only related to the flux and current, similar to the control method of the DC motor. , can get very high control performance. For the permanent magnet synchronous motor, the rotor flux position is the same as the rotor mechanical position, so that the magnetic flux position of the motor rotor can be known by detecting the actual position of the rotor, so that the vector control of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is compared with the vector control of the asynchronous motor. Simplified. Servo drive control AC permanent magnet servo motor (pmsm) servo drive can work in current (torque), speed, position control mode when controlling AC permanent magnet servo motor. The control structure block diagram of the system is shown in Figure 4. Since the AC permanent magnet servo motor (pmsm) is excited by a permanent magnet, its magnetic field can be regarded as constant; at the same time, the motor speed of the AC permanent magnet servo motor is the synchronous speed, that is, its rotation. The difference is zero. These conditions greatly reduce the complexity of the mathematical model of the AC servo drive when driving the AC permanent magnet servo motor. As can be seen from Figure 4, the system is based on measuring the two-phase current feedback (ia, ib) and motor position of the motor. Combine the measured phase currents (ia, ib) with the position information, and change the coordinates (from the a, b, c coordinate system to the rotor d, q coordinate system) to obtain the id and iq components, respectively, and enter the respective current regulators. . The output of the current regulator undergoes a reverse coordinate change (converted from the d, q coordinate system to the a, b, c coordinate system) to obtain a three-phase voltage command. Through the three-phase voltage command, the control chip obtains 6 channels of pwm wave output to the power device after the reverse and delay, and controls the motor to run. In different command input modes, the command and feedback are passed through the corresponding control regulators to obtain the next level of reference commands. In the current loop, the torque current component (iq) of the d, q axis is the output of the speed control regulator or external reference. In general, the flux component is zero (id=0), but when the speed is greater than the limit value, a higher speed value can be obtained by weakening the magnetic field (id “0â€). Convert from a, b, c coordinate system to d, q coordinate system with Clarke and Park transformation to achieve; from d, q coordinate system to a, b, c coordinate system is Clark and Parker The inverse transformation is implemented. 1, torque control The torque control mode is to set the external output torque of the motor shaft by external analog input or direct address assignment. 2, position control The position control mode generally determines the rotation speed by the frequency of the externally input pulse, and determines the angle of rotation by the number of pulses. Some servos can directly assign speed and displacement by communication. Since the position mode has strict control over speed and position, it is generally applied to positioning devices. 3, speed mode The rotation speed can be controlled by the analog input or the frequency of the pulse. The speed mode can also be positioned when the outer ring PID of the upper control device is controlled, but the position signal of the motor or the position signal of the direct load must be given to the upper position. Feedback is used for calculations. Modern AC servo systems were first applied to aerospace and military fields, such as artillery and radar control. Gradually entered the industrial and civilian sectors. Industrial applications mainly include high-precision CNC machine tools, robots and other general-purpose CNC machines, such as textile machinery, printing machinery, packaging machinery, medical equipment, semiconductor equipment, postal machinery, metallurgical machinery, automated assembly lines, and various special equipment. The industries with the largest servo usage are: machine tools, food packaging, textiles, electronic semiconductors, plastics, printing and rubber machinery, totaling more than 75%.
A TPU Screen Protector made of the super toughness of the honeycomb structure. Its unique ultra-soft properties allow it to cover the most complex curves and contours in a device.
Screen Protector For iPhone,Hydrogel Film for iPhone,Hydrogel Screen Protector For iPhone,TPU Screen Protector For iPhone,iPhone Screen Protector Shenzhen Jianjiantong Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.jjthydrogelmachine.com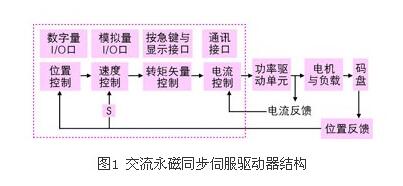

The self-healing design of the Hydrogel Screen Protector can protect the display screen of the device from damage, leave no air bubbles, and maintain the sensitivity of the touch screen. Advanced anti-fingerprint and dust- and oleophobic overlays keep your screen smudge- and dirt-free. This overlay is also important in providing maximum touch sensitivity for improved high-speed glide and optimal touch response.
The optical transparency of the Hydrogel Film is more than 90%, showing you the most original screen color and bringing the most realistic visual experience.
If you want to know more about the product information of the Hydrogel Screen Protector for iPhone, please click the product details to view the parameters, model, picture, price and other information of the iPhone Screen Protector.
Whether you are a group or an individual, we will do our best to provide you with accurate and comprehensive information about Hydrogel Screen Protectors!